Introduction
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is revolutionizing the construction and real estate industry in India. As the country moves towards smart cities and sustainable development, BIM has become essential for modern engineering practices. This comprehensive guide covers everything Indian engineers need to know about BIM implementation, from basic concepts to advanced applications.
BIM is crucial for India’s construction sector because it addresses key challenges like cost overruns, project delays, and quality issues that have historically plagued the industry. With the government’s push for infrastructure development and smart cities, understanding BIM is no longer optional for construction professionals.
Who should read this guide?
- Fresh engineering graduates entering construction
- Experienced professionals transitioning to BIM
- Real estate developers and project managers
- Students working on construction-related projects
- Government officials involved in infrastructure planning

What is BIM? Understanding the Fundamentals
Definition and Core Components
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital process that creates and manages information throughout a building’s lifecycle. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, BIM creates intelligent 3D models that contain comprehensive data about every building component.
BIM evolved from Computer-Aided Design (CAD) systems but offers far more capabilities. While CAD produces simple drawings, BIM creates data-rich models that include material properties, costs, schedules, and performance characteristics.
BIM vs Traditional CAD – Key Differences
| Aspect | Traditional CAD | BIM |
|---|---|---|
| Visualization | 2D drawings | 3D intelligent models |
| Data Integration | Limited | Comprehensive building data |
| Collaboration | File-based sharing | Real-time collaboration |
| Error Detection | Manual checking | Automated clash detection |
| Cost Estimation | Separate process | Integrated quantity takeoff |
| Updates | Manual coordination | Automatic synchronization |
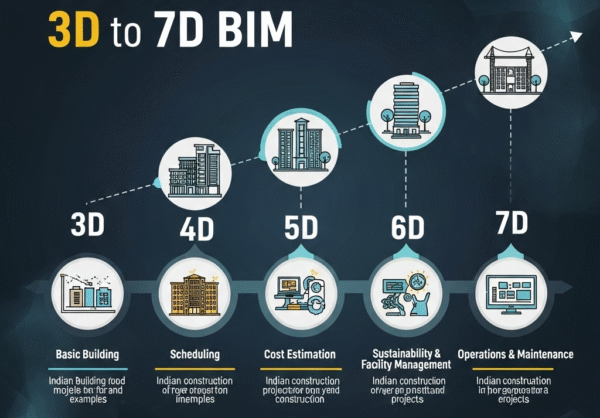
BIM Dimensions Explained with Indian Examples
3D BIM – Geometric Modeling Creates three-dimensional visual representations of buildings. The new Terminal 2 at Mumbai Airport used 3D BIM for complex architectural visualization.
4D BIM – Time/Scheduling Adds time dimension to 3D models, showing construction sequences. Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) uses 4D BIM to plan underground station construction without disrupting surface traffic.
5D BIM – Cost Management Integrates cost data with 3D models for real-time budget tracking. Larsen & Toubro uses 5D BIM to reduce project costs by 15% through better cost control.
6D BIM – Sustainability Focuses on energy analysis and environmental impact. Tata Housing projects use 6D BIM to achieve GRIHA green building certifications.
7D BIM – Facility Management Manages building operations and maintenance post-construction. Smart cities like Pune use 7D BIM for infrastructure asset management.
Key BIM Software and Tools for Indian Market
Popular Commercial BIM Software
Autodesk Revit Most widely used BIM software in India, supporting architectural, structural, and MEP design. Excellent integration with Indian standards like IS 456 for concrete design.
Bentley AECOsim Building Designer Popular for large infrastructure projects. Used extensively by government agencies like CPWD (Central Public Works Department).
Tekla Structures Preferred for steel and precast concrete detailing. Widely used in industrial construction across India.
Free and Open-Source BIM Tools
FreeCAD Excellent starting point for engineering students and small firms. Supports parametric 3D modeling with BIM capabilities.
BonsaiBIM Combines Blender’s powerful modeling with IFC-based BIM workflows. Growing popularity among Indian startups.
BIM Plugins for Indian Standards
Several plugins ensure compliance with Indian building codes:
- IS 456 compliance plugins for concrete design
- National Building Code (NBC) 2016 integration
- CPWD specification libraries
- GST calculation modules for accurate cost estimation
BIM Implementation in Indian Construction Industry
Current Adoption Trends
BIM adoption in India is accelerating, driven by government initiatives and industry demand. The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) promotes BIM for smart city projects, while major developers like Lodha Group and Sobha Limited have mandated BIM for all new projects.
Government Initiatives
Smart Cities Mission Over 100 smart cities are implementing BIM for urban planning and infrastructure development.
RERA Compliance Real Estate Regulation and Development Act encourages BIM adoption for transparent project delivery.
CPWD Mandate Central Public Works Department is gradually mandating BIM for government construction projects above certain values.
Residential Project Case Studies
Lodha Group Implementation
- Reduced design errors by 40%
- Improved project delivery timelines by 20%
- Enhanced customer visualization through 3D walkthroughs
Sobha Limited’s BIM Journey
- Standardized design processes across projects
- Improved quality control through clash detection
- Reduced material wastage by 15%
Tata Housing Success
- Integrated sustainability analysis from design stage
- Achieved faster statutory approvals
- Improved coordination between architectural and MEP teams
Infrastructure Projects
Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC)
- Used BIM for complex underground station design
- Reduced rework by 30% through clash detection
- Improved coordination with existing utilities
Highway Projects National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) increasingly uses BIM for:
- Complex interchange design
- Bridge and tunnel coordination
- Environmental impact assessment
Airport Development
- New Bengaluru International Airport Terminal used BIM
- Coordinated complex MEP systems
- Optimized passenger flow through simulation
BIM Workflow and Best Practices
BIM Execution Plan (BEP) for Indian Projects
A comprehensive BEP should include:
Project Information
- Client requirements and objectives
- Project scope and deliverables
- Timeline and milestones
Team Structure
- BIM coordinator and modelers
- Discipline leads and responsibilities
- Communication protocols
Modeling Standards
- Level of Development (LOD) requirements
- Naming conventions
- File organization structure
Technology Infrastructure
- Software selection and versions
- Hardware requirements
- Cloud collaboration platforms
Quality Control
- Model checking procedures
- Clash detection protocols
- Review and approval processes
Level of Development (LOD) Standards
LOD 100 – Conceptual Design Basic massing and conceptual elements. Used for feasibility studies and initial approvals.
LOD 200 – Schematic Design Generic building systems with approximate quantities. Suitable for preliminary cost estimation.
LOD 300 – Design Development Specific building assemblies with accurate dimensions. Used for detailed design coordination.
LOD 400 – Construction Documentation Detailed fabrication and installation information. Required for construction and procurement.
LOD 500 – As-Built Model Field-verified representation of completed construction. Used for facility management.
Collaboration Platforms
Autodesk BIM 360
- Cloud-based model coordination
- Real-time collaboration across teams
- Mobile access for site teams
Trimble Connect
- Cross-platform collaboration
- Model viewing and markup tools
- Integration with field data collection
Bentley ProjectWise
- Enterprise-level project delivery
- Document management integration
- Workflow automation
BIM for Cost Estimation and Quantity Takeoff
5D BIM Implementation
5D BIM integrates cost data directly with 3D models, enabling:
- Real-time cost updates as design changes
- Automated Bill of Quantities (BOQ) generation
- Life-cycle cost analysis
Automated Quantity Takeoff Benefits
Traditional manual measurement methods are prone to errors and time-consuming. BIM automation provides:
- 95%+ accuracy in quantity calculations
- 60% reduction in estimation time
- Consistent measurement standards
- Real-time quantity updates
GST Integration in BIM
Modern BIM software includes GST calculation modules that:
- Apply correct tax rates for different materials
- Generate GST-compliant invoices
- Track tax implications of design changes
- Integrate with accounting systems
BIM for Structural and MEP Design
Structural BIM with Indian Standards
Reinforcement Detailing per IS 2502
- Automated rebar placement and scheduling
- Compliance with Indian concrete cover requirements
- Integration with structural analysis software
Concrete Design per IS 456
- Automated design checks for beams and columns
- Grade-specific concrete properties
- Indian load combinations and safety factors
MEP Coordination and Clash Detection
HVAC Systems
- Ductwork routing optimization
- Load calculation integration
- Energy analysis for GRIHA compliance
Plumbing Design
- Pipe sizing per IS 1172
- Water demand calculations
- Drainage system optimization
Electrical Systems
- Cable tray routing
- Load distribution analysis
- IS 732 compliance for electrical installations
Prefab and Modular Construction
BIM optimizes prefabricated construction by:
- Precise component manufacturing
- Reduced on-site assembly time
- Quality control in factory conditions
- Faster project delivery
BIM for Project Management
4D BIM for Construction Scheduling
Integration with project management software like Primavera P6 enables:
- Visual construction sequencing
- Resource optimization
- Progress tracking and reporting
- What-if scenario analysis
Safety Planning with BIM
Hazard Identification
- Virtual safety inspections
- Fall protection planning
- Equipment placement optimization
Safety Training
- Virtual reality safety training
- Site-specific hazard awareness
- Emergency evacuation planning
Facility Management Applications
Asset Tracking
- Equipment maintenance schedules
- Warranty information management
- Spare parts inventory
Space Management
- Occupancy tracking
- Space utilization analysis
- Move management
Energy Management
- Utility consumption monitoring
- Energy audit automation
- Maintenance optimization
Material and Manpower Requirements
Typical Materials in BIM Projects
Hardware Requirements
- High-performance workstations with dedicated graphics cards
- Large monitors for detailed modeling work
- Network infrastructure for file sharing
- Backup systems for data security
Software Licenses
- BIM software subscriptions (₹2-5 lakhs per seat annually)
- Plugin licenses for specialized functions
- Cloud collaboration platform subscriptions
Manpower Structure
Manager
- Overall BIM strategy and implementation
- Standards development and enforcement
- Team coordination and training
- Salary range: ₹15-25 lakhs per annum
Coordinators
- Model coordination and clash detection
- Quality control and standards compliance
- Interdisciplinary communication
- Salary range: ₹8-15 lakhs per annum
Modelers
- 3D model creation and documentation
- Drawing production and updates
- Design visualization
- Salary range: ₹4-8 lakhs per annum
Training Requirements
- 40-80 hours initial BIM software training
- Ongoing skill development programs
- Certification courses from recognized institutes
Deliverables at Each Project Stage
Pre-Construction Phase
Conceptual Design (LOD 100)
- Massing studies and site analysis
- Feasibility reports with preliminary costs
- Regulatory approval submissions
- Environmental impact assessments
Design Development (LOD 200-300)
- Detailed architectural drawings
- Structural design calculations
- MEP system layouts
- Clash detection reports
- Updated cost estimates
- Construction phasing plans
Construction Documentation (LOD 400)
- Complete drawing sets
- Specifications and details
- Final quantity takeoffs
- Procurement schedules
- Construction sequence plans
Construction Phase
Model Updates
- As-built model maintenance
- Request for Information (RFI) responses
- Change order documentation
- Progress monitoring reports
Quality Control
- Clash detection reports
- Model validation checks
- Construction sequencing updates
- Site coordination meetings
Post-Construction Phase
As-Built Documentation (LOD 500)
- Final as-built models
- Equipment manuals and warranties
- Maintenance schedules
- Facility management handover
Facility Management
- Asset databases
- Maintenance planning
- Energy performance monitoring
- Space management systems
Stakeholders and Communication Matrix
Key Project Stakeholders
Internal Team
- Project Manager
- Design Team (Architects, Engineers)
- BIM Coordinator
- Site Execution Team
- Quality Control Team
External Stakeholders
- Client/Developer
- Regulatory Authorities
- Contractors and Subcontractors
- Suppliers and Vendors
- End Users
Communication Protocols
Regular Meetings
- Weekly BIM coordination meetings
- Monthly progress reviews with stakeholders
- Quarterly technology updates and training
Reporting Structure
- Daily: Site progress updates via mobile apps
- Weekly: Clash detection and resolution reports
- Monthly: Project dashboard with KPIs
- Quarterly: ROI analysis and benefits realization
Documentation Standards
- Standardized meeting minutes templates
- Model change logs and version control
- Issue tracking and resolution protocols
- Knowledge sharing and lessons learned
Value Engineering Opportunities
Cost-Saving Techniques
Design Optimization
- Structural system optimization reduces material usage by 10-15%
- Standardized components lower manufacturing costs
- Modular design approaches reduce construction time
Construction Efficiency
- Clash detection prevents costly rework
- Accurate quantity takeoffs reduce material waste
- Optimized construction sequencing saves time
Lifecycle Cost Reduction
- Energy-efficient design reduces operational costs
- Predictive maintenance extends asset life
- Space optimization maximizes utilization
Real-World Case Study: Smart City BIM Implementation
Project Overview
Project: Bhubaneswar Smart City Command Center
Client: Bhubaneswar Development Authority
Timeline: 18 months (2020-2022)
Budget: ₹150 crores
BIM Implementation: Comprehensive 4D and 5D modeling
Challenges Faced
Technical Challenges
- Integration of multiple smart city systems
- Complex MEP coordination for data centers
- Seismic design requirements for critical infrastructure
Process Challenges
- Limited BIM expertise in local teams
- Coordination between multiple agencies
- Compliance with both national and international standards
Solutions Implemented
Technology Solutions
- Cloud-based collaboration platform for multi-location teams
- Integrated IoT sensors for real-time monitoring
- VR-based design reviews with stakeholders
Process Improvements
- Comprehensive BIM training for all team members
- Weekly coordination meetings with all disciplines
- Standardized quality control checkpoints
Results and Key Takeaways
Quantifiable Benefits
- 25% reduction in project timeline
- 20% cost savings through clash detection
- 95% accuracy in quantity estimation
- Zero major rework during construction
Qualitative Improvements
- Enhanced stakeholder communication
- Improved design quality and coordination
- Better project risk management
- Successful technology transfer to local teams
Lessons Learned
- Early BIM adoption crucial for maximum benefits
- Continuous training essential for team effectiveness
- Stakeholder buy-in critical for successful implementation
- Data management strategies must be established upfront
Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Common BIM Implementation Risks
Technical Risks
- Software compatibility issues between disciplines
- Data loss due to inadequate backup systems
- Model corruption during collaborative work
- Hardware performance limitations
Process Risks
- Resistance to change from traditional methods
- Inadequate training leading to poor adoption
- Unclear roles and responsibilities
- Insufficient quality control procedures
Financial Risks
- High initial investment in software and training
- Extended learning curve affecting productivity
- Ongoing subscription costs for software licenses
- Potential project delays during transition period
Mitigation Strategies
Technology Risk Mitigation
- Standardize on compatible software platforms
- Implement robust backup and version control systems
- Regular model validation and quality checks
- Invest in adequate hardware infrastructure
Process Risk Mitigation
- Comprehensive change management programs
- Phased implementation starting with pilot projects
- Clear BIM execution plans and responsibilities
- Regular training and skill development programs
Financial Risk Mitigation
- Detailed ROI analysis and business case development
- Phased investment approach to spread costs
- Partner with experienced BIM consultants initially
- Government incentives and subsidies for technology adoption
Training and Skill Development
Best BIM Training Institutes in India
NITTTR (National Institute of Technical Teachers Training and Research)
- Government-recognized certification programs
- Comprehensive curriculum covering all BIM aspects
- Affordable fees for engineering professionals
- Pan-India presence with local training centers
- Industry-focused practical training
- Job placement assistance programs
Online Learning Platforms
- Autodesk University free online courses
- LinkedIn Learning BIM specializations
- YouTube channels with practical tutorials
Certification Programs
Autodesk Certified Professional
- Industry-recognized credentials
- Software-specific expertise validation
- Career advancement opportunities
International Certifications
- BuildingSMART Professional Certification
- BIM Institute certifications
- PMI-BIM professional credentials
Recommended Learning Path
Beginner Level (0-6 months)
- BIM fundamentals and concepts
- Basic 3D modeling in Revit or similar software
- Drawing production and documentation
- Simple clash detection exercises
Intermediate Level (6-18 months)
- Advanced modeling techniques
- Multi-disciplinary coordination
- 4D and 5D BIM applications
- Family creation and customization
Advanced Level (18+ months)
- BIM management and leadership
- Custom workflow development
- API programming and automation
- Enterprise BIM implementation
Future of BIM in India
Government Mandates and Policies
National BIM Standards The National Institute of Construction Development and Research (NICDC) is developing comprehensive BIM standards for India, expected to be implemented by 2026.
State Government Initiatives
- Tamil Nadu mandates BIM for projects above ₹50 crores
- Karnataka promotes BIM for smart city projects
- Maharashtra planning BIM requirements for RERA projects
Emerging Technologies
Artificial Intelligence Integration
- Automated design optimization
- Predictive analytics for project risks
- Intelligent scheduling and resource allocation
Machine Learning Applications
- Pattern recognition for design efficiency
- Cost prediction based on historical data
- Quality control through image recognition
IoT and Smart Building Integration
- Real-time sensor data integration with BIM models
- Predictive maintenance systems
- Energy optimization through IoT feedback
Market Projections
The Indian BIM market is expected to grow at 20% CAGR, reaching ₹2,500 crores by 2028. Key growth drivers include:
- Government infrastructure investments
- Private sector adoption for competitive advantage
- Skilled workforce development initiatives
- Technology cost reduction and cloud accessibility
BIM Standards and Compliance
National Standards Development
Indian BIM Standards Framework
- Based on international ISO 19650 standards
- Adapted for Indian construction practices
- Integration with existing IS codes and NBC requirements
Key Standard Components
- Information modeling requirements
- Exchange protocols and formats
- Quality assurance procedures
- Security and data management
International Standards Adoption
ISO 19650 Implementation
- Information management throughout asset lifecycle
- Collaborative working methodologies
- Common data environment requirements
- Risk management frameworks
IFC (Industry Foundation Classes)
- Open standard for BIM data exchange
- Vendor-neutral format for interoperability
- Support for complex building information
Green Building Integration
GRIHA Integration
- Automated energy analysis for rating
- Material selection for environmental compliance
- Water usage optimization tools
LEED Compliance
- Energy modeling integration
- Material tracking for credits
- Construction waste management
Career Opportunities and Salary Trends
BIM Job Roles in Indian Market
Manager (₹15-30 lakhs/annum)
- Strategic BIM implementation
- Team leadership and training
- Client relationship management
- Technology roadmap development
Coordinator (₹8-18 lakhs/annum)
- Model coordination and quality control
- Interdisciplinary clash resolution
- Standard implementation and compliance
- Technical support and troubleshooting
Architect/Engineer (₹6-15 lakhs/annum)
- 3D modeling and documentation
- Design development and analysis
- Visualization and presentation
- Technical drawing production
Analyst (₹5-12 lakhs/annum)
- Quantity takeoff and cost estimation
- Energy analysis and optimization
- Data analysis and reporting
- Performance monitoring
Growth Opportunities
Career Progression Path
- BIM Modeler → BIM Coordinator → BIM Manager
- Specialized tracks: VDC Manager, Digital Construction Lead
- Entrepreneurial opportunities: BIM consulting services
Skills in High Demand
- Multi-disciplinary BIM expertise
- Cloud collaboration platform management
- Programming and automation skills
- Project management and leadership
Practical Tips for Getting Started
Free Learning Resources
YouTube Channels
- Balkan Architect (Revit tutorials)
- The BIM Guys (industry insights)
- Autodesk Building Solutions (official tutorials)
Online Courses
- Coursera BIM specializations
- edX construction management courses
- NPTEL building technology courses
Practice Projects
- Residential building modeling exercises
- Small commercial project tutorials
- Infrastructure design case studies
Building a BIM Portfolio
Project Types to Include
- Residential building (architectural focus)
- Commercial project (MEP coordination)
- Infrastructure element (structural emphasis)
- Renovation project (existing conditions modeling)
Documentation Standards
- Before and after comparisons
- Process workflows and methodologies
- Problem-solving approaches
- Lessons learned summaries
Networking and Professional Development
Professional Organizations
- Indian Building Congress (IBC)
- Institution of Engineers (India)
- Association of Consulting Civil Engineers (ACCE)
Industry Events
- Annual BIM conferences and exhibitions
- Software vendor user meetings
- Government policy workshops
- International collaboration forums
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling represents the future of construction in India. As the industry moves towards digitalization, BIM adoption becomes crucial for competitive advantage and project success. The comprehensive benefits of BIM – from cost reduction and quality improvement to enhanced collaboration and sustainability – make it an essential tool for modern construction professionals.
The journey to BIM implementation requires careful planning, adequate training, and strong stakeholder commitment. However, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial challenges. Organizations that embrace BIM today will be better positioned for future growth and success in India’s rapidly evolving construction landscape.
Success in BIM implementation depends on understanding both the technology and the process changes required. This guide provides the foundation for making informed decisions about BIM adoption, whether you’re a student beginning your career, a professional transitioning to new methods, or an organization planning comprehensive digital transformation.
The future of Indian construction is digital, collaborative, and data-driven. BIM is not just a technology – it’s a methodology that transforms how we conceive, design, build, and manage our built environment. Embracing this transformation today ensures readiness for tomorrow’s challenges and opportunities.
External References
- National Building Code of India 2016
- IS 456: Code of Practice for Concrete Design
- GRIHA Rating System Documentation
- Smart Cities Mission Guidelines
Industry Publications
- Construction World Magazine
- Indian Infrastructure Magazine
- Smart Cities India Publication
- Building Materials & Technology Magazine